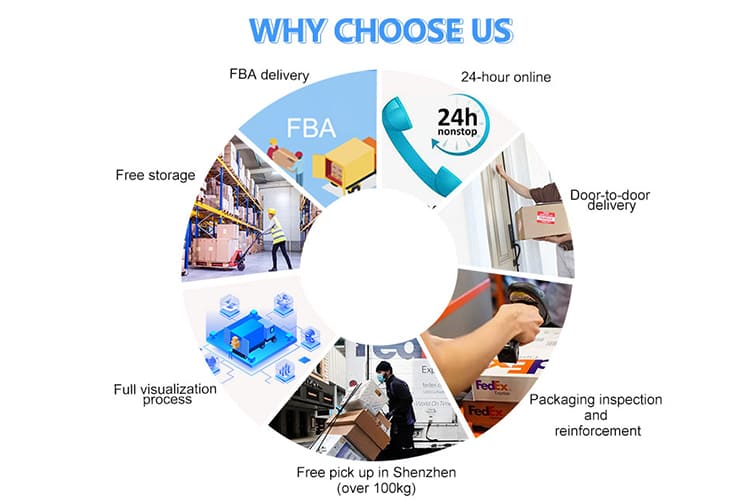
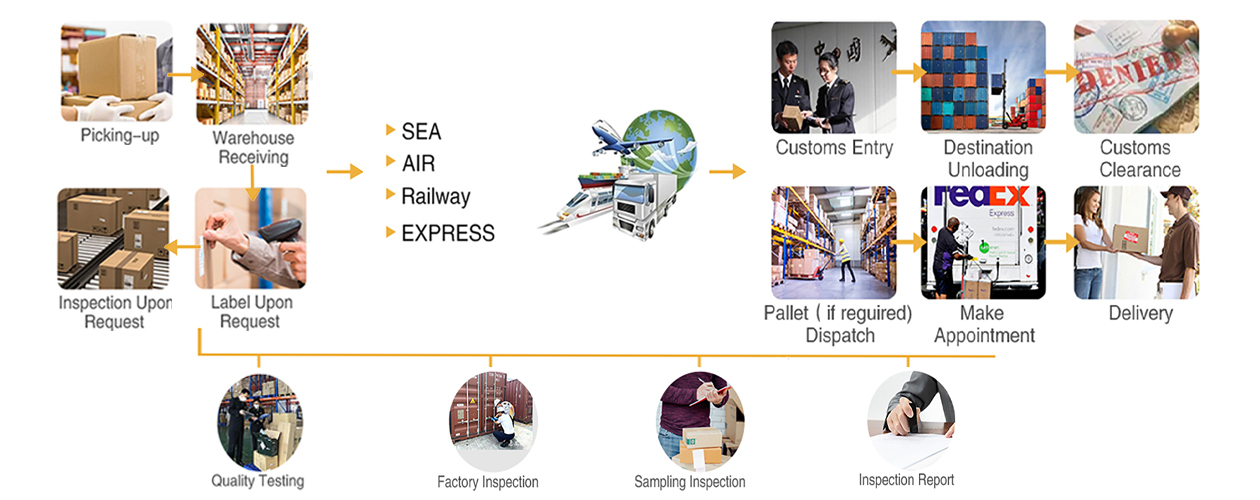
Description
Air Freight
Characteristics:
- Speed: Air freight is the fastest of all shipping methods, typically used for urgent or high-value goods. Delivery time usually ranges from 3 to 7 business days.
- Suitable Cargo: Ideal for light, small, and high-value items such as electronics, luxury goods, and medical supplies.
- Higher Cost: Air freight is more expensive compared to other modes of transport, especially for large and heavy items.
Advantages:
- Quick delivery, making it suitable for time-sensitive shipments.
- Extensive global route coverage, allowing for fast delivery to most countries and regions.
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs, particularly uneconomical for large or heavy cargo.
- Vulnerable to delays caused by weather, flight schedules, and other factors.
Sea Freight
Characteristics:
- Lower Cost: Sea freight is the most cost-effective option among the four modes, especially for bulk goods or non-urgent shipments.
- Longer Transit Time: Typically takes weeks or even longer, depending on the distance between the origin and destination.
- Suitable Cargo: Ideal for heavy, large, and relatively low-value goods such as furniture, industrial equipment, and bulk commodities.
Advantages:
- High capacity, making it suitable for large shipments.
- Cost-effective, especially for non-urgent cargo.
Disadvantages:
- Longer transit times, leading to extended shipping cycles.
- Potential delays due to port handling, customs inspections, and route adjustments.
Truck Freight
Characteristics:
- High Flexibility: Truck freight offers door-to-door service, making it particularly suitable for short-haul or cross-border land transportation.
- Moderate Speed: Faster than sea freight but slower than air freight, typically used for regional land transport, especially in areas like Europe and North America.
- Suitable Cargo: Suitable for medium to short-distance transport and a wide range of goods, including general trade goods, food, and building materials.
Advantages:
- Door-to-door service, eliminating the need for transshipment and reducing cargo handling.
- Highly adaptable, capable of reaching remote areas or inland cities without ports.
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs, particularly for long-distance transport.
- Potential delays due to road conditions, traffic regulations, and border controls.
Rail Freight
Characteristics:
- Moderate Speed: Rail freight’s transit speed falls between air and sea freight, commonly used for long-distance land transport, especially in regions with well-developed cross-border rail networks, such as the China-Europe rail route.
- Moderate Cost: Cheaper than air freight but more expensive than sea freight, making it suitable for goods that require relatively fast delivery at a controlled cost.
- Suitable Cargo: Ideal for bulk commodities, machinery, vehicles, furniture, and other goods.
Advantages:
- Relatively fast, especially for cross-continental transport, saving time compared to sea freight.
- High capacity, suitable for transporting bulk goods, and environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages:
- Limited by existing rail networks, making it less flexible.
- Potential delays due to border inspections, track gauge changes, and other logistical challenges.
Summary
- Air Freight is ideal for high-value, urgent goods, prioritizing speed.
- Sea Freight is best for non-urgent, bulk goods, prioritizing cost.
- Truck Freight offers high flexibility, ideal for regional land transport and door-to-door service.
- Rail Freight
Contact Us Today
Ready to experience seamless door-to-door express shipping from China? Contact us today to learn more about our services and get started with your shipment. Let us handle the logistics while you focus on growing your business!

Applications of DAP, DDU, and DDP in Express Delivery
Express delivery services often utilize these Incoterms to provide tailored solutions for international shipping. Here’s how each term applies:
1. DAP in Express Delivery
-
DAP is commonly used for express deliveries where the seller arranges fast and efficient transportation to the buyer’s location.
-
It is ideal for buyers who prefer to handle customs clearance themselves or have established relationships with local customs brokers.
2. DDU in Express Delivery
-
DDU is suitable for express shipments when the buyer wants to control the customs process or has specific requirements for duty payment.
-
It is often used in industries where import duties vary significantly, such as electronics or luxury goods.
3. DDP in Express Delivery
-
DDP is the most convenient option for buyers, as the seller manages all aspects of delivery, including customs and duties.
-
It is widely used in e-commerce and retail, where buyers expect a seamless delivery experience.
Advantages of Using DAP, DDU, and DDP
For Sellers:
-
DAP: Allows sellers to maintain control over transportation while limiting responsibility for customs clearance.
-
DDU: Reduces the seller’s liability for import duties and taxes, making it a cost-effective option.
-
DDP: Enhances customer satisfaction by offering a fully managed delivery service.
For Buyers:
-
DAP: Provides flexibility in handling customs clearance and duty payments.
-
DDU: Enables buyers to manage customs processes and potentially reduce costs.
-
DDP: Offers a hassle-free experience, as the seller handles all logistics and regulatory requirements.